Introduction
In the world of internet connectivity and data transfer, users often encounter the terms Mbps and MBps, which are crucial for understanding speed and performance. While they may seem similar, these two measurements represent different things and can significantly affect how you interpret your internet speed, download times, and overall network efficiency.
Confusion between Mbps and MBps can lead to misunderstandings when comparing internet plans, running speed tests, or calculating file download times. Knowing the difference ensures accurate expectations and better planning for activities like streaming, gaming, cloud backups, or large file transfers.
This comprehensive guide explains the difference between Mbps and MBps, their real-world impact, and practical examples to help users make informed decisions about internet speed, data usage, and network performance.
What Is Mbps?
Mbps stands for Megabits per second, a unit used to measure network data transfer speed. Internet service providers typically advertise speeds in Mbps. It indicates how many millions of bits of data can be transmitted per second over a network.
Why Mbps Matters
- Determines internet performance for browsing, streaming, and downloads
- Impacts video call quality and online gaming responsiveness
- Helps compare different internet plans
Real-World Example
A 100 Mbps internet connection can transfer up to 100 million bits of data per second. However, this does not directly translate to the number of megabytes you download in a given time.
What Is MBps?
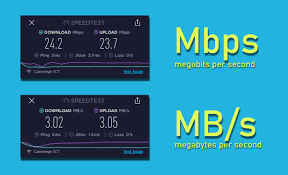
MBps stands for Megabytes per second, a unit representing data size transmitted per second. Since 1 byte = 8 bits, MBps is eight times larger than Mbps.
Why MBps Matters
- Used to measure actual file download or upload speeds on devices
- Helps calculate transfer time for large files
- Reflects real-world data transfer rather than network signaling speed
Real-World Example
Downloading a 1 GB file with a speed of 10 MBps would take roughly 100 seconds, whereas confusing it with 10 Mbps would result in an 800-second download time.
Mbps vs MBps: Key Differences
Understanding the difference between Mbps and MBps is crucial for interpreting network performance accurately.
| Aspect | Mbps | MBps |
|---|---|---|
| Stands for | Megabits per second | Megabytes per second |
| Usage | Network speed, ISP plans | File transfer speed, storage devices |
| Conversion | 8 Mbps = 1 MBps | 1 MBps = 8 Mbps |
| Focus | Transmission rate | Data volume received/sent |
Common Misconceptions
Many users confuse Mbps with MBps when calculating download times or comparing internet speeds. Always check the unit to avoid misinterpretation.
How to Convert Between Mbps and MBps
Conversion is straightforward once you understand the 8-bit relationship.
Formulas:
- MBps = Mbps ÷ 8
- Mbps = MBps × 8
Example
An internet speed of 80 Mbps quals 10 MBps in file transfer speed, which helps estimate realistic download times.
Why Knowing the Difference Matters
Understanding Mbps vs MBps helps in:
- Choosing the right internet plan for your needs
- Estimating download/upload times for files
- Optimizing home or office network setups
- Avoiding frustration when experiencing slower-than-expected speeds
Practical Example
Streaming a 4K video requires around 25 Mbps. If a user misinterprets this as 25 MBps, they might overestimate the speed, expecting faster performance than reality.
Tips for Optimizing Internet Speed Based on Mbps/MBps
To get the most out of your internet connection, consider the following:
- Choose an ISP plan that meets your data usage requirements
- Use speed tests to measure Mbps accurately
- Optimize router placement and hardware for consistent performance
- Monitor downloads in MBps to set realistic expectations
Conclusion
Understanding Mbps vs MBps is essential for accurately measuring internet speed and predicting real-world performance. Mbps measures network signaling speed, while MBps reflects actual data transfer rates. By knowing the difference and applying proper conversions, users can choose suitable internet plans, optimize network setups, and set realistic expectations for downloads, streaming, and online activities.
FAQs
1. What does Mbps stand for?
Megabits per second, used to measure network speed.
2. What does MBps stand for?
Megabytes per second, representing actual data transfer rate.
3. How do I convert Mbps to MBps?
Divide the Mbps value by 8.
4. Why do ISPs advertise speeds in Mbps?
Because it represents network signaling speed, which is industry standard.
5. How does MBps affect download times?
It shows the actual speed at which data is downloaded or uploaded, helping estimate realistic times.